Products

 BIGFOOT 15
Learn More
BIGFOOT 15
Learn More




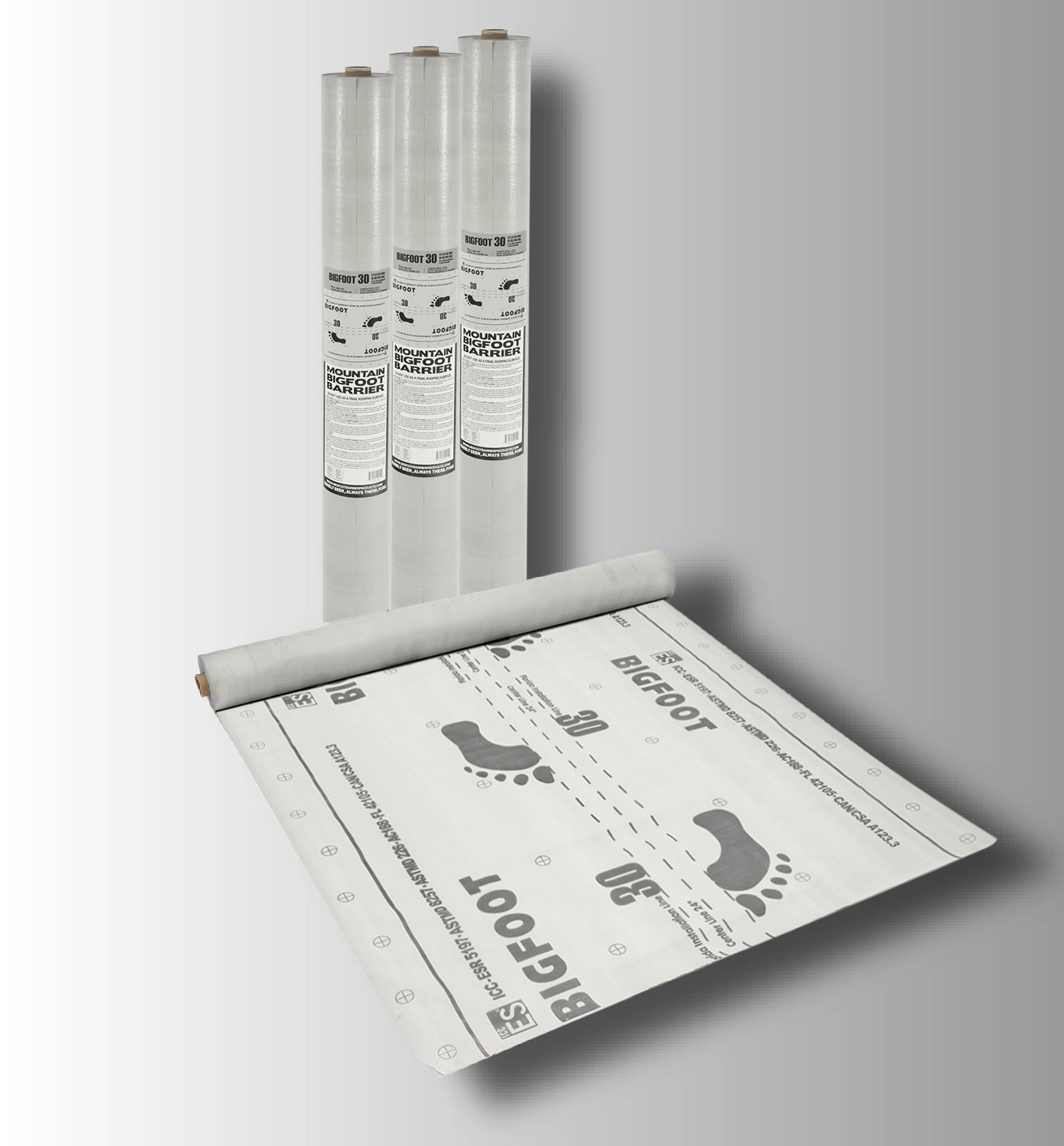
 BIGFOOT 30
Learn More
BIGFOOT 30
Learn More



 BIGFOOT 180
Learn More
BIGFOOT 180
Learn More




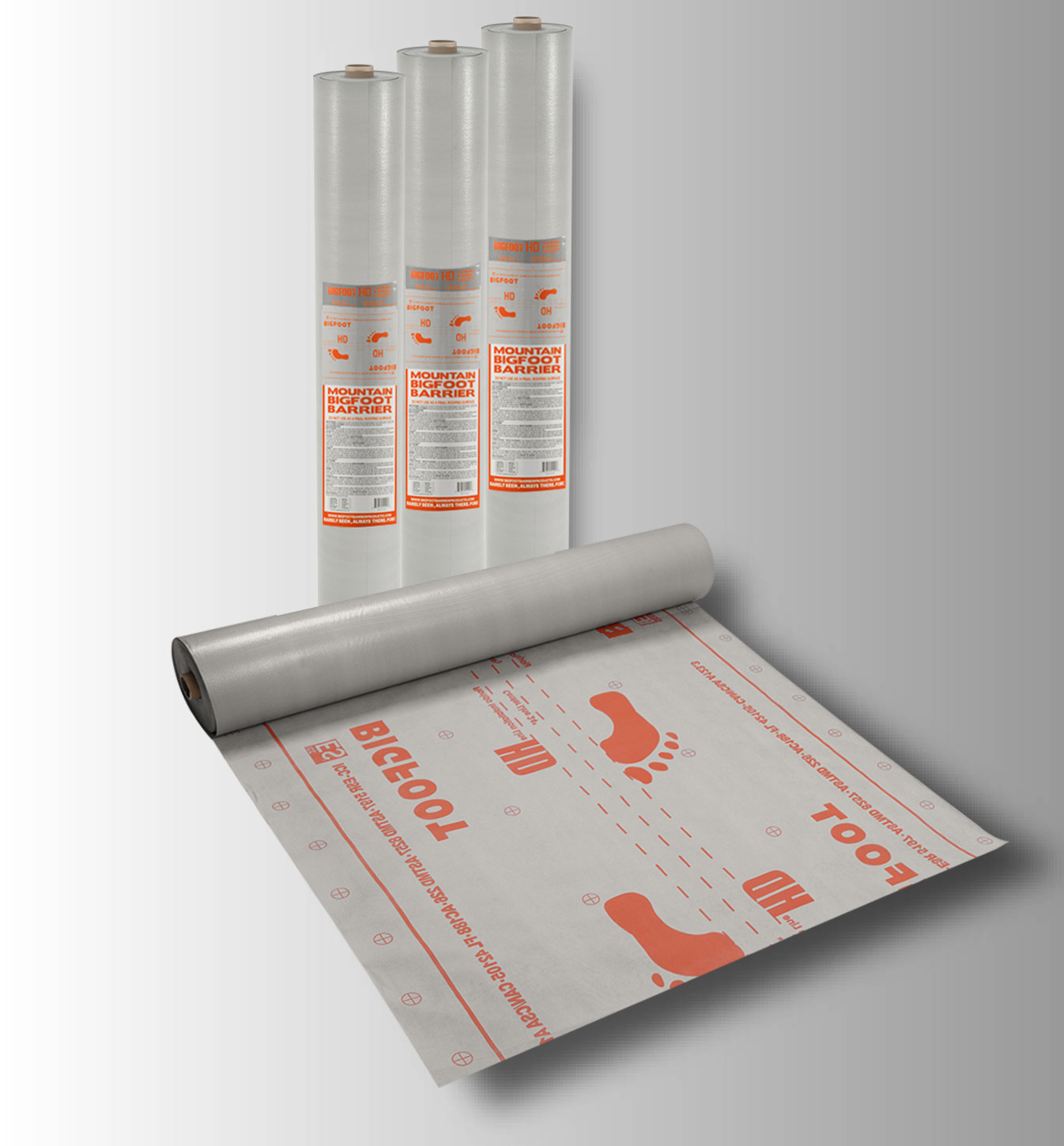
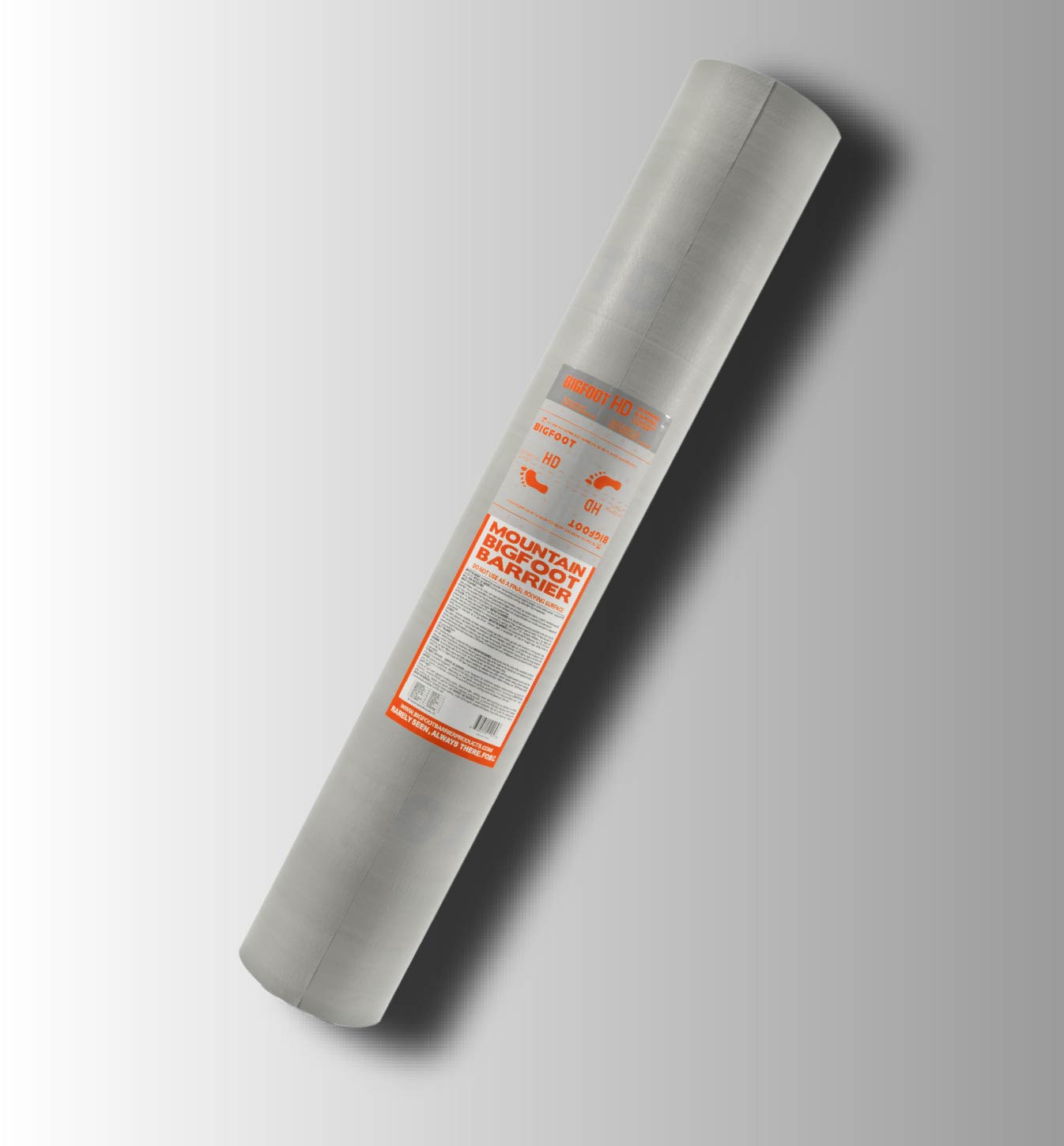
 BIGFOOT HD
Learn More
BIGFOOT HD
Learn More





 BIGFOOT 15
BIGFOOT 15
BIGFOOT 15 IS DESIGNED FOR USE UNDER MECHANICALLY ATTACHED ASPHALT SHINGLES, METAL ROOFING AND TILE, REPLACE OF 15# OR 30# FELT
ROLL LENGTH
250'
ROLL WIDTH
48"
ROLL COVERAGE
10 SQ
ROLL WEIGHT
19 LBS
ROLL S/PALLET
72
PALLET WEIGHT
1368 LBS
UV EXPOSURE GUARANTEE
90 DAYS
LIMMITED WARRANTY
25 YRS




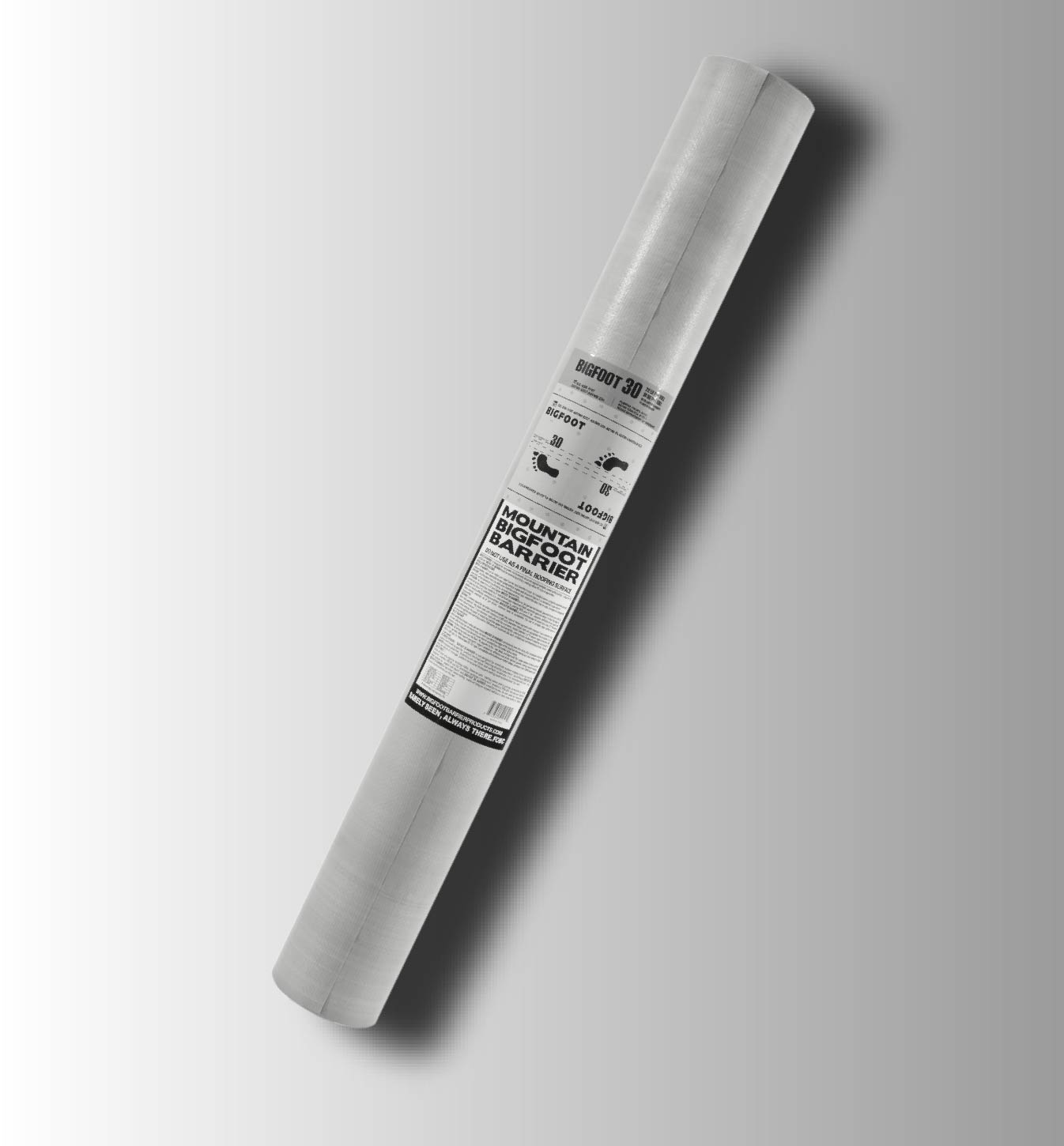
 BIGFOOT 30
BIGFOOT 30
BIGFOOT 30 IS DESIGNED FOR USE UNDER MECHANICALLY ATTACHED ASPHALT SHINGLES, RESIDENTAL METAL AND TILE, REPLACE OF 15# OR 30# FELT
ROLL LENGTH
250'
ROLL WIDTH
48"
ROLL COVERAGE
10 SQ
ROLL WEIGHT
22 LBS
ROLLS/PALLET
64
PALLET WEIGHT
1408 LBS
UV EXPOSURE GUARANTEE
180 DAYS
LIMMITED WARRANTY
30 YRS




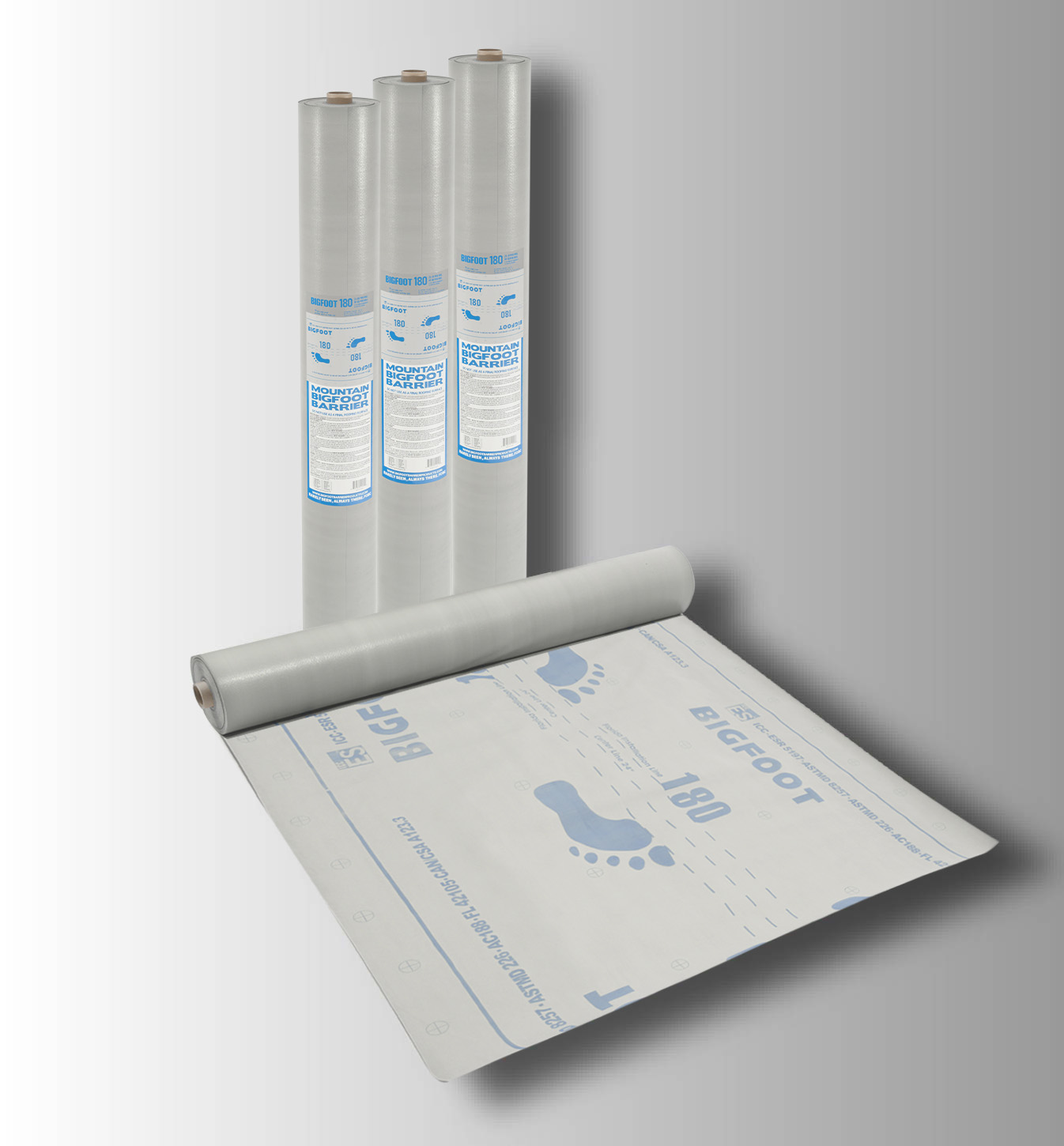
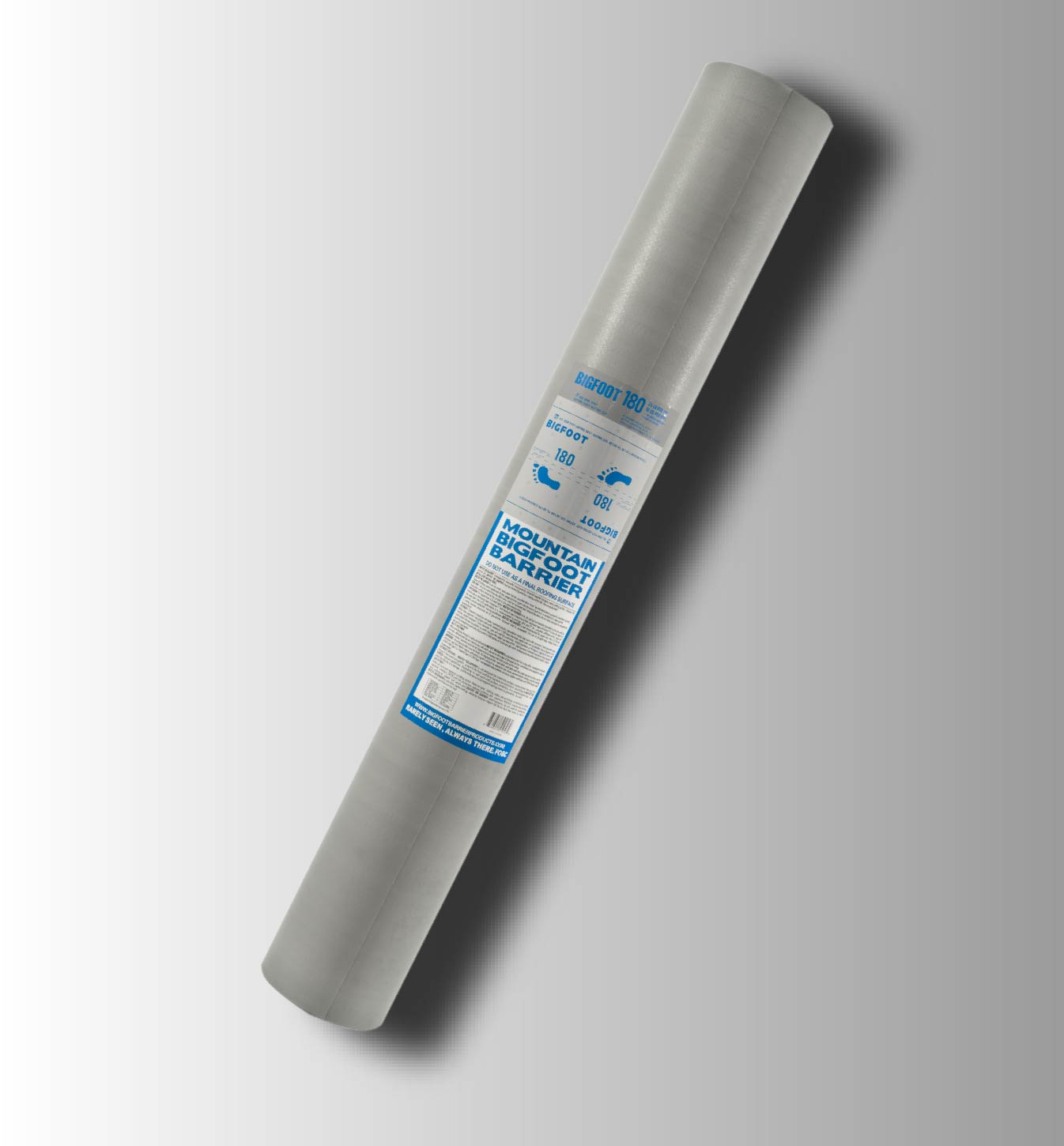
 BIGFOOT 180
BIGFOOT 180
BIGFOOT 180 IS DESIGNED FOR USE UNDER MECHANICALLY ATTACHED ASPHALT SHINGLES, METAL ROOFING AND TILE, SLATE, REPLACE OF 15# OR 30# FELT
ROLL LENGTH
250'
ROLL WIDTH
48"
ROLL COVERAGE
10 SQ
ROLL WEIGHT
26 LBS
ROLLS/PALLET
56
PALLET WEIGHT
1456 LBS
UV EXPOSURE GUARANTEE
180 DAYS
LIMMITED WARRANTY
40 YRS




 BIGFOOT HD
BIGFOOT HD
BIGFOOT HD IS DESIGNED FOR USE UNDER MECHANICALLY ATTACHED ASPHALT SHINGLES, METAL ROOFING AND TILE, SLATE,CONCRETE & CLAY TILES,REPLACE OF 15# OR 30# FELT
ROLL LENGTH
250'
ROLL WIDTH
48"
ROLL COVERAGE
10 SQ
ROLL WEIGHT
38 LBS
ROLLS/PALLET
30
PALLET WEIGHT
1140 LBS
UV EXPOSURE GUARANTEE
365 DAYS
LIMMITED WARRANTY
50 YRS








 Back
Back





